FRStaticGuardファブリック
帯電防止生地は、静電気の蓄積を防ぐように設計された繊維の一種です。製造施設やクリーンルームでは、繊細な電子機器への損傷を防ぐためによく使用されます。.
静電気防止生地とは何ですか?
帯電防止布(静電気防止布とも呼ばれる)は、静電気の蓄積を防ぐ素材です。その帯電防止特性は、電荷の消散と中和という2つのメカニズムに基づいています。.
物体が接地されると、導電性繊維のコロナ放電によって布地に帯電した静電気は中和され、残留静電気は導電性繊維を介して地面に放散されます。導電性繊維が接地されていない場合でも、微弱なコロナ放電によって静電気を放散することができます。.
静電気の危険性
衣服の着用性能の影響
異なる素材の衣服から発生する静電気により、衣服同士が絡まり、着心地が悪くなることがあります。また、衣服と皮膚が逆の電荷を帯びると、衣服同士がくっつき、歩行が困難になることもあります。.
偶発的な事故の原因
合成繊維の衣類を着用すると、大量の静電気が発生し、衣類の表面に蓄積される可能性があります。蓄積された静電気は、空気層を破壊して火花を発生させる可能性があります。火花のエネルギーは、周囲の可燃性ガスや爆発性ガスに引火するのに十分なほどで、火災や爆発につながる可能性があります。.
繊維製品の品質への影響
繊維を解繊する工程では、静電気の影響で繊維が機械フレーム、配管、その他の表面に付着し、出力繊維層の厚さが不均一になるだけでなく、絡み合い、圧縮、巻き込みによる生産上の問題も発生します。.

静電気防止生地を使用する業界:

研究所

クリーンルーム

ATEXエリア
自動車
静電気防止繊維素材の原理:
静電気が発生する原因は一般的に 2 つあります。
1. 接触により発生する静電気。.
2.誘導により発生する静電気。.
接触によって発生する静電気は、主に電荷の移動によって発生します。2つの物体が接触して擦れ合うと、一方の物体の表面には正電荷が蓄積され始め、もう一方の物体の表面には負電荷が帯電し、静電気が発生します。.
誘導によって発生する静電気は、導電性物質が導体または絶縁体の近くにあるときに発生します。導電性物質に最も近い導体または絶縁体の側に電荷が蓄積され始めます。誘導が長時間続くと、導体または絶縁体の正電荷と負電荷がtelに分離され、静電気が発生します。.
どちらの場合も、電荷移動効果と呼ばれます。静電気防止とは、帯電防止生地が電荷移動効果を最小限に抑え、静電気の蓄積を防ぎ、製品との摩擦や接触を軽減することで、静電気の蓄積を防ぐという目的を達成することを指します。一般的に用いられる3つの方法を以下に示します。
繊維製品の帯電防止方法
繊維の帯電防止処理は、主に繊維の導電性を高め、周囲の湿度を改善することから始まります。最も基本的かつ重要な方法は、繊維の電気抵抗を下げ、導電性を高めることです。繊維の帯電防止処理には、主に以下の3つの方法があります。
布地に帯電防止剤を処理する。繊維に親水性基をグラフトして改質し、親水性繊維と混紡または織り合わせる。導電性繊維と混紡または織り合わせる。.
最初の2つの方法は、生地の吸湿性を高め、断熱性を低下させ、静電気の放散を早めるというメカニズムです。そのため、乾燥した環境や繰り返し洗濯をした場合、その効果は持続せず、顕著にならない可能性があります。.
3つ目の方法は、繊維製品の静電気問題を永続的かつ効率的に解決できます。静電気防止作業服などの特殊機能性衣料に活用できます。.
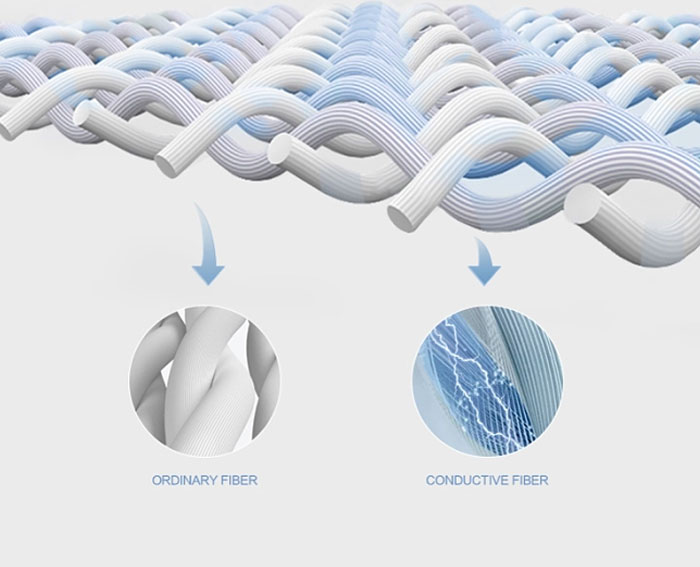
帯電防止繊維および織物の製造
1. 外部静電気防止方法
繊維の表面に外部から帯電防止剤を付着させる方法を表面処理といい、一時的帯電防止処理と永続的帯電防止処理に分類できます。.
(1)一時的な帯電防止処理。一般的に、繊維の製造・加工中の静電気による干渉を防ぐために、外部からのスプレー、含浸、コーティングなどの方法が用いられる。.
(2)耐久制電加工。耐久制電加工は、熱処理による架橋、あるいは樹脂担体への付着により、繊維表面に逆電荷のイオンを引き寄せることで実現されます。これにより、一定の耐久性、耐洗濯性、耐摩擦性などの特性が得られます。.
2. 内部静電気防止方法
繊維に帯電防止剤を組み込むには、次の 3 つの方法が使用されます。
(1)紡糸前に繊維ポリマーを改質する。通常、親水性化合物は紡糸前に繊維モノマーと共重合される。.
(2)ポリマーに帯電防止剤を混合するブレンド紡糸法、または複合紡糸法を用いる。.
(3)繊維表面に導電性金属やカーボンブラック(表面処理の一種)をコーティングしたり、複合紡糸法を用いてカーボンブラックを含んだ帯電防止繊維を製造したりします。.

BEGOODTEX帯電防止生地の利点:
高い導電性と優れた静電気性能。最細6.5µmの金属繊維は優れた導電性を有し、静電気を効果的に放散します。.
着心地が良く、極細で非常に柔らかい繊維と糸が衣服にシームレスに溶け込み、高い快適性を保ちます。.
優れた洗濯性 工業洗濯を何回行っても衣類の特性や帯電防止性能は変わりません。.
静電気による悪影響からさまざまな電気機器を保護するには、ESD を放散して電気機器の誤動作を防ぐことが不可欠です。.
長寿命: 優れた耐久性により、生地の寿命が長くなります。.
固有難燃性(難燃性)+帯電防止生地の用途

1. 電子産業:静電気防止生地は、生産工程における静電気による干渉を防ぐため、生産現場の作業服や手袋に広く使用されています。また、電子部品を静電気による危険から保護し、部品の品質と安定した性能を確保します。.
2. 医療・ヘルスケア:静電気防止生地は、手術着、手術帽、手術靴カバーなどに使用されます。これらの製品は、静電気の蓄積の問題を効果的に軽減できます。.
3. 石油化学産業:石油化学産業では、静電気防止生地を静電気防止衣類、手袋、靴カバーなどの保護具に利用し、静電気によって引き起こされる火災や爆発を軽減します。.
4. 航空宇宙:静電気防止生地は、静電気による干渉や損傷を防ぐための静電気防止衣類、手袋、靴カバーなどの保護具に航空宇宙業界で活用されています。.
5. 電力業界:静電気防止生地は、静電気によって引き起こされる火災や爆発を防ぐための静電気防止衣類、手袋、靴カバーなどの保護具として電力業界で利用できます。.
6. 自動車製造:自動車製造業界では、静電気による干渉や自動車電子機器への損傷を防ぐために、作業服や手袋などの保護具に静電気防止生地を活用できます。.
関連製品
-
-
-
森林消防用NFPA 2112認証アラミド3A耐火ジャケット OEM/ODM工場直送
#0302 グレー#0602 レッド#0702 オレンジ -
幅: 150 cm | 重量: 280 g/m²
280 GSM 高可視モダクリル FR リップストップ生地 –難燃性および帯電防止安全作業服
BG-L19-901 -
幅: 150 cm | 重量: 200 g/m²
200g/m² アラミド 1414 帯電防止 FR ファブリック ブラック 保護繊維
BG-L51-101 -
幅: 150 cm | 重量: 160 g/m²
160g/m² アラミド 1414 帯電防止 FR ファブリック ブラック 工業用布
BG-L50-101 -
幅: 150 cm | 重量: 150 g/m²
150g/m² アラミド 1414 帯電防止 FR 生地 ブラック 軽量布
BG-L49-101 -
幅: 150 cm | 重量: 200 g/m²
200g/m² アラミド 1414 帯電防止 FR 生地 ブラック 工業用作業服
BG-L48-101 -
幅: 150 cm | 重量: 200 g/m²
200gsm 耐火アラミドビスコースモダクリル生地 | 作業服用帯電防止2色保護布
#1102 ブルー#1103 ダークブルーBG-L43













